CBCV, or cannabichromevarin, is one of about 140 similar chemical compounds (cannabinoids) present in all cannabis varieties. It is a propyl homologue of cannabichromene (CBC), is non-intoxicating and does not induce a euphoric high like delta-8, delta-9 or any other isomer THC. I apologize for any confusion. If recent developments have provided new information about CBCV, I wouldn’t have that information available in my training data since my knowledge was last updated in September 2021. It’s possible that there have been advancements or discoveries about CBCV since that time. It’s always best to refer to the latest scientific research and reputable sources for accurate and up-to-date information about specific cannabinoids and their potential effects.
So what is CBCV?
Thank you for providing more information about CBCV. It seems you have a good understanding of its characteristics and potential effects. If you have any further questions or if there’s anything else you’d like to know, feel free to ask!
CBCV has the chemical structure C19H26O2 and it is a propyl cannabinoid, which means its structure has a tail with three carbon atoms. In contrast, CBC, which is the pentyl cannabinoid counterpart of CBCV, has a tail with five carbon atoms. Cannabis plants biosynthesise CBCV via naturally occurring divarictic acid. In contrast, CBC is biosynthesised via olivetolic acid. Asian hemp and hashish commonly have higher levels of propyl cannabinoids, including CBCV.
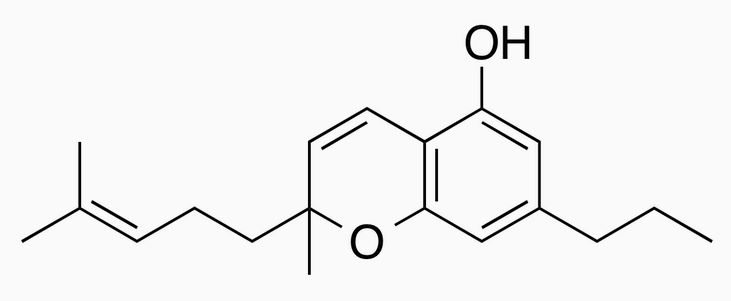
Molecular structure of CBCV cannabichromevarin
It is a minor cannabinoid. Unlike cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), CBCV is a minor cannabinoid, meaning it makes up <1% of the total cannabinoid profile of cannabis;
CBCV is derived from cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA). The conversion of CBCVA to CBCV occurs when exposed to heat, also known as the decarboxylation process, in which a carbon atom is released from the carbon chain. In other words, CBCVA ceases to be an acid and is converted into a full-fledged cannabinoid;
CBCV was discovered by researchers at the University of Nagasaki while analysing the Meao variant, a strain of marijuana grown in Thailand. Since its discovery, research has been limited. Very little is known about its effects, benefits or safety;
Current CBCV research
Current research on CBCV is limited and there are very few preclinical or clinical studies on how it interacts with your body. The lack of research is not shocking. Major cannabinoids such as CBD, THC and cannabigerol (CBG) have captured most of the attention when it comes to research, and most of the minor cannabinoids have been left out.
That’s not to say that research on CBCV doesn’t exist – you’re limited to one very recent study on its potential anticonvulsant abilities in combination with other minor cannabinoids;
CBCV as a potential anticonvulsant
In a recent preclinical study, researchers discovered that the combination of CBCV, CBCVA, CBCA, and CBC has significant anticonvulsant properties in test subjects of mice experiencing seizures induced by hypothermia. The research team believes that CBCV and all other CBC derivatives “may be part of the mechanism by which artisanal hemp oils are anticonvulsant in patients.”.

Products that may be of interest to you
Benefits of CBCV: What is it good for?
The benefits of CBCV are still somewhat unknown. However, judging by the limited research mentioned above, we can safely say that it has the potential as a promising anticonvulsant, especially when combined with other cannabinoids. Furthermore, since CBCV is nearly identical to CBC, we presume that they share very similar benefits.
Research shows that CBC binds to the vanilloid receptor type 1 (TRPV1) and transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1). Activation of both receptors can influence pain perception and prevent enzymes from breaking down anandamide. Anandamide is an endogenous cannabinoid (endocannabinoid) naturally produced by the brain. It’s also known as the “bliss molecule,” creating feelings of happiness and pleasure. CBC’s prevention of anandamide breakdown leads to prolonged and more effective elevation of mood.
Researchers also suggest that the modulation of TRP channels by CBC could combat COVID-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines in the lungs and blood by up to 50%. CBC is also a selective agonist of the cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), which could prove beneficial for inflammation modulation.
Finally, CBC is thought to have antidepressant and anti-stress properties in rodent test models, especially in conjunction with CBD, THC and CBG.
Effects of CBCV: How do you feel?
In addition to being a non-intoxicating cannabinoid without the ability to induce euphoric excitement, very little is known about how you feel after consuming CBCV. However, since CBCV shares many similarities with CBC, it is assumed that their effects are nearly identical.
The effects of CBC include:
- Luck
- Increase mood
- Relaxation
- Stress reduction
How does CBCV compare to THC and CBDA?
- CBCV vs THC– While CBCV does not induce a euphoric high, THC does, by binding to cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors located in the brain and central nervous system. Unlike CBCV, THC is not a homologue of CBC, nor is it a propyl cannabinoid. The two have different chemical structures. CBCV and THC have potential anticonvulsant benefits for patients with epilepsy. However, THC may also be proconvulsant and a poor controller of seizure episodes.
- CBCV vs CBDA– Like CBCV, CBDA does not produce a euphoric high, nor does it affect your thinking, memory, or judgment. CBDA is the acidic form of CBD before the decarboxylation process. CBCV is the decarboxylated form of CBCVA. Neither CBCV nor CBDA is believed to have much affinity with your cannabinoid receptors and act as weak receptor agonists. Rather, they both have a relationship with other receptors separate from your endocannabinoid system. CBCV potentially interacts with your TRPV1 and TRPVA1 receptors, while CBDA affects your 5-HT serotonin receptors.
Conclusion
As with most minor cannabinoids, CBCV remains a mystery to researchers, industry professionals and consumers. However, CBCV’s similarity to CBC and its benefits make it a promising cannabinoid, especially when combined with other essential cannabinoids, including CBD, CBG and THC;