When people talk about cannabinoids, many people think of THC and CBD. However, these are only 2 of the 113 identified compounds in marijuana. Some cannabinoids are more well known, some are less talked about, this is mainly because of their potential in medicine. Research on cannabinoids is fascinating because we are learning more about how they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. So what are cannabinoids? They are a diverse class of chemicals that lead to a huge range of effects associated with cannabis. THC and CBD are known for their health benefits. However, other cannabinoids, such as CBC, or cannabichromene, also act on the endocannabinoid system. This interaction between cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors promotes balance in your body;
What is the CBC?
CBC is a potent non-psychoactive cannabinoid. CBC, like THC and CBD, has been shown to promote human brain growth by increasing the viability of developing brain cells in a process known as neurogenesis;
CBC plays an important role in the anti-cancer and anti-tumour capabilities of cannabis. CBC also fights inflammation, but without activating any of the endocannabinoid receptors in the body. For this reason, the medicinal powers of CBC are significantly enhanced when combined with other cannabinoids such as THC or CBDs, which activate endocannabinoid receptors in the brain and throughout the body. Although CBC is one of the most important cannabinoids, most people don’t even know it exists. It was first discovered in 1966 and is one of the naturally occurring phytocannabinoids of cannabis;
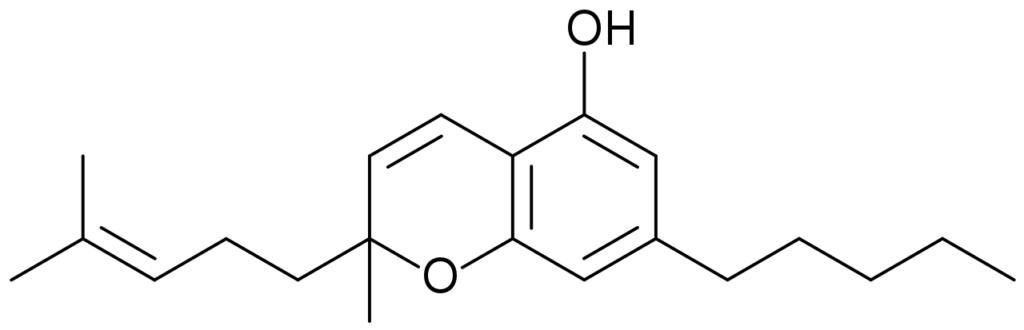
In some cases, CBC can account for up to 64% of a plant’s cannabinoid profile. However, they often select plants with a high THC content. Therefore, very few of them contain high levels of CBC. In terms of function, CBC has several similarities with THC and CBD. Like the two most well-known cannabinoids, CBC develops through the enzymatic conversion of the precursor CBG (cannabigerol). CBGA (cannabigerol acid, which decarboxylates to CBG) reacts with enzymes in one of the plant’s glandular trichomes. The resulting reaction forms CBCA (cannabichromenic acid), which then decarboxylates to CBC. Decarboxylation is the scientific term for “a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide”;
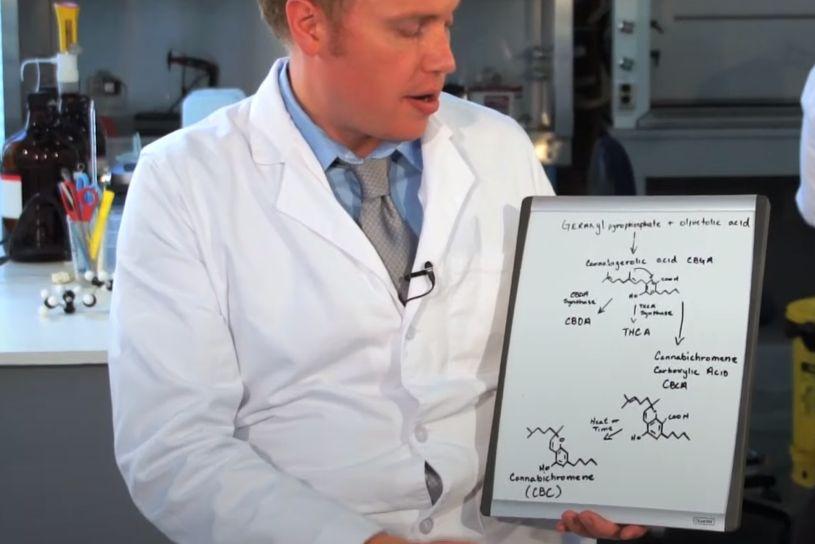
What is the difference between CBC and other cannabinoids?
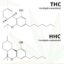
If the molecular formula C21H30O2 sounds familiar to you, you’re right. It is the chemical formula of THC, CBD and CBC. Interestingly, the atoms in the molecule have a slightly different arrangement;
Although several cannabinoids share the same formula, subtle changes in structure ensure that they will act in different ways. For example, THC differs from CBC and CBD in its ability to bind to CB1 receptors. This helps to achieve the famous psychoactive effect associated with smoking marijuana;
CBC is similar to CBD because it does not bind well to cannabinoid receptors such as CB1 and CB2. As you probably know, CB1 receptors are mainly in the brain. THC is one of the cannabinoids that activates CB1, causing the famous euphoric feeling. CBC also does not bind well to CB2 receptors. However, it interacts with a number of other receptors such as TRPV1 and TRPA1.
Activation of these receptors increases the level of endocannabinoids in your body. An example of this is an increase in the production of anandamide, which is known as the happiness molecule;
CBC achieves this by interfering with processes that tend to degrade these receptors. CBC increases the activity of cannabinoid receptors that occur naturally in cannabis, thereby indirectly activating the body’s cannabinoid receptors;
In contrast, THC and other psychoactive compounds directly bind to and affect the relevant receptors, particularly CB1 and CB2;
Products that may be of interest to you
What is the CBC used for?
CBC has several advantages as a standalone cannabinoid. However, research suggests that it is most effective when working with other cannabinoids because of the accompanying effect. The idea behind the entourage effect is that individual cannabinoids offer more effect when they work together than when they work individually. For example, THC and CBD combine well. The CBD in marijuana acts to prevent intoxication caused by THC;
CBC has many of the same therapeutic effects as CBD. Since it is not intoxicating, it creates an exciting alternative. Studies show that CBC can help with many health problems, from chronic pain to acne;

Health benefits of CBC
Relief from chronic pain
A 2011 study found that CBC effectively blocks pain associated with collagen-induced osteoarthritis. As with many other cannabinoids, the effect of CBC on inflammation is very different from that of NSAIDs;
A 2010 study by DeLong et al. also produced some interesting findings. The study showed that when CBC was combined with THC, it provided an additive effect. This led to a much greater anti-inflammatory response than when the cannabinoid was used alone.
In the study, the research team analyzed the effects of CBC on edema. They found that the cannabinoid reduced overall swelling. Interestingly, the effect occurred independently of CB receptors. This is because the antagonists prevented THC from working in the same way, but did not block CBC.
Neurogenesis
CBC may not turn a fool into a genius, but it does promote neurogenesis. A 2013 study by Shinjyo and Di Marzo found this out. The duo analyzed the effects of neural stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) from adult mice outside the body. They found that these particular cells differentiate into many other cells, helping the brain grow and regenerate. The results also showed that CBC improved NSPC function.
Why is this significant? One of the cells that NSPCs differentiate into is called an astroglial cell. These cells are essential for maintaining homeostasis in the brain. They perform a number of functions, such as providing defense against oxidative stress and the direction of neurotransmitters. Oxidative stress, toxicity and inflammation create neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. Thus, in theory, the presence of CBCs improves the viability of NSPCs. NSPCs then differentiate into astroglial cells, which may counteract the problems that lead to neurological diseases.
Cancer
Cannabichromene may be a powerful cancer fighter and the reason may be its interaction with the body’s natural endocannabinoid, anandamide. CBC also appears to inhibit the absorption of anandamide, allowing it to remain in the bloodstream longer. A recent study in which tumour growth was initiated in mice (a two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis model) showed that cannabinoids can be effective in inhibiting both inflammation and tumour growth. Since anandamide has been shown to fight breast cancer in vitro and in vivo, it shows promise that CBC and other cannabinoids may one day become chemopreventive agents.
CBC as a potential cancer fighter was first published in a 2006 study that examined cannabinoids other than THC and their possible effects on cancer. While THC is known for its anti-cancer properties for several different forms of cancer, its potent psychotropic properties may make it difficult to use chemotherapy. Research so far has found that CBC is the second most potent cannabinoid in inhibiting the growth of new cancer cells (CBG was the most effective);
Antidepresivum
For a long time, all we heard about was how THC and CBD can help with anxiety disorders and depressed. However, the CBC appears to have a similar positive impact. A 2010 study by El-Alfy et al. showed that rats performed better on stress tests after a CBC load. Chronic stress is known to be one of the main triggers of depression. It also shows that CBC works best for depression when combined with THC and CBD.
Antibacterial properties
It seems strange, but most of the best CBC research was done in the 80s. A study published in 1981 by Turner and Elsohly found that CBC had impressive antibacterial properties. CBC has helped fight a number of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococcus and E. coli.
A more recent study by researchers in Italy and the UK in 2008 found that CBC and other cannabinoids were at least as effective against MRSA as strong drugs such as Vancomycin. Moreover, cannabinoids didn’t punish you with a host of unwanted side effects.
Fights acne
If your expensive acne creams aren’t working, you might want to try CBC. A September 2016 study by Olaha and co. found that CBC is an excellent acne inhibitor.
As you may know, excessive sebum production and inflammation of the sebaceous glands are the main culprits in the development of acne. CBC fights acne due to its anti-inflammatory properties and also slows down the production of lipids in the sebaceous gland. Arachidonic acid (AA) is needed to produce lipogenesis, but CBC reduces the rate of AA production. Although we need more data, it seems that CBC could become one of the best agents for the treatment of acne.
Are there any CBC-specific products on the market?
Today, CBC is usually found in younger plants. However, most growers grow their plants to have high levels of CBD or THC. This makes it hard to find marijuana with significant CBC content. So far, there are no marijuana strains specifically bred for high CBC content. As a result, it is difficult to find products with a high CBC content. One possibility is to allow the marijuana plant to degrade its THC into cannabinol (CBN). CBN has similar medicinal properties to CBC;
Conclusion
A few decades ago, CBC was the second most abundant compound found in marijuana in a few select strains. Today, however, relatively few strains contain the compound that seems to work best with THC, CBD and others. Still, research has shown that CBC itself may be beneficial as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Most of the useful CBC research was done in the 80s. Since then, THC and CBD have taken over the interest of the scientific community. However, awareness of CBC is steadily increasing and it is likely that it will receive more attention in the future and perhaps in a few years we will find it in common health care products;